Multiple-Connection Telnet Server (run as a service)
Put it all together - this program was compiled from a number of different articles on this service as well as a little modification of my own. It allows you to create a telnet server service to run commands or return data on your servers. Runs as a Windows NT/2000 service on Port 26 (by default) and even allows multiple users to be connected at once.
Original Author: Daniel M. Hendricks
Assumptions
To use this code, you must HAVE these components:
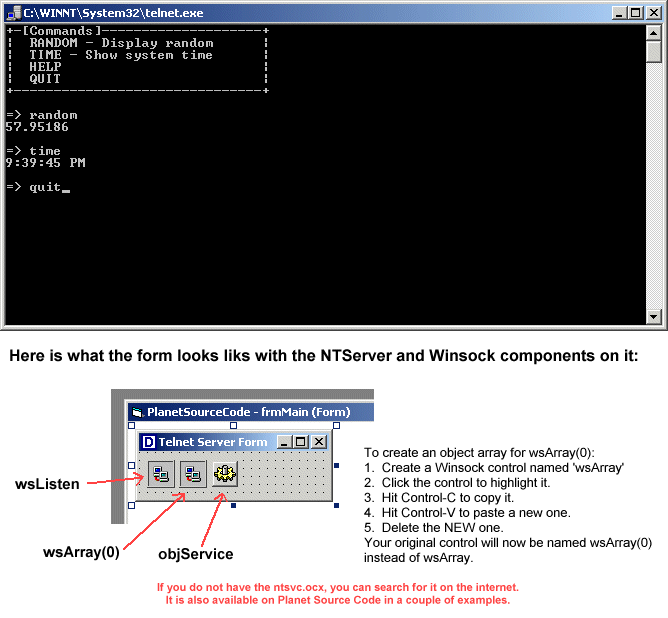
1. Microsoft NT Service Control (ntsvc.ocx)
2. Microsoft Winsock Control 6.0 (SP4) (mswinsck.ocx)
To use this code, you must DO the following:
1. Create a single, main form
2. Add two WINSOCK controls, one called 'wsListen' and
another WINSOCK component array called 'wsArray(0)'
In other words, you should have two WINSOCK compon-
ents on your form.
3. Create one NTService object on the main form called
'objService'.
4. Copy the following code to your form
- After coding, compile the program
- Run from the Command Prompt:
programname.exe -install
- Run from the Command Prompt:
net start telnetd
If you did everything right, you should be able to
telnet to your computer!
USAGE: State -> Run -> telnet localhost 26
API Declarations
Public strCommand As String
Code
Public strCommand As String
Private Sub Form_Load()
'BE SURE TO READ THE "ASSUMES" SECTION ABOVE FIRST!
objService.DisplayName = "Telnet Server Demo"
objService.ServiceName = "telnetd"
wsListen.LocalPort = 26
'This code is displayed if the user runs the program from
'the command-line.
If Trim$(Command$) <> "" Then
Select Case UCase$(Trim$(Command$))
Case "-INSTALL"
If objService.Install Then
MsgBox "Result: " & App.Title & " successfully installed as a Windows NT Service." & vbCrLf & "Service Name: " & objService.ServiceName, vbInformation, "Install Complete, Please Re-Start Application"
Else
MsgBox "Result: " & App.Title & " FAILED to installed as a Windows NT Service." & vbCrLf & "Service Name: " & objService.ServiceName & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & "Solutions: Check to see if the service is allready installed. If so, run " & App.EXEName & " -uninstall to remove it.", vbInformation, "Install Failed, Please Re-Start Application"
End If
End
Case "-UNINSTALL"
If objService.Uninstall Then
MsgBox "Result: " & App.Title & " successfully uninstalled as a Windows NT Service." & vbCrLf & "Removed Service Name: " & objService.ServiceName, vbInformation, "UnInstall Complete, Please Re-Start Application"
Else
MsgBox "Result: " & App.Title & " FAILED to Uninstalled as a Windows NT Service." & vbCrLf & "Service Name: " & objService.ServiceName & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & "Solutions: Check to see if the service is installed. If not, run " & App.EXEName & " -install to install it.", vbInformation, "UnInstall Failed, Please Re-Start Application"
End If
End
Case Else
MsgBox "Valid Syntax: " & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & "-install To Install " & App.Title & " as a WinNT Service" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & "-uninstall To UN-INSTALL " & App.Title & " from the WinNT Service List", vbInformation, "Invalid Syntax: Aborting Program Launch"
End Select
End If
objService.ControlsAccepted = svcCtrlPauseContinue
objService.StartService
Me.Hide
End Sub
Private Sub objService_Start(Success As Boolean)
'This code is executed when the service is started
On Error GoTo ErrHandler
Success = True
wsListen.Listen
Exit Sub
ErrHandler:
'If service fails, write an event to the system log.
Call objService.LogEvent(svcMessageError, svcEventError, "[" & _
Err.Number & "] " & Err.Description)
Resume Next
End Sub
Private Sub wsArray_DataArrival(Index As Integer, ByVal bytesTotal As Long)
'This code determinds what to do based on user input
Dim strData(100) As String
On Error GoTo ErrorHandler
'Get the current character user typed
wsArray(Index).GetData strData(Index), vbString, bytesTotal
If strData(Index) = vbCrLf Or strData(Index) = vbCr Then
Select Case UCase(wsArray(Index).Tag)
Case "RANDOM"
'Display a random number
wsArray(Index).SendData vbCrLf & Rnd(1) * 100 & vbCrLf
Case "TIME"
'Display the current time
wsArray(Index).SendData vbCrLf & Time() & vbCrLf
Case "HELP"
wsArray(Index).SendData vbCrLf
Call ShowMenu(Index)
Case "QUIT"
wsArray(Index).Tag = ""
wsArray(Index).Close
Exit Sub
End Select
wsArray(Index).Tag = ""
wsArray(Index).SendData vbCrLf & "=> "
ElseIf Asc(strData(Index)) = 8 Then 'Backspace was pressed
If Not wsArray(Index).Tag = "" Then
'Remove one character from current input
wsArray(Index).Tag = Left(wsArray(Index).Tag, Len(wsArray(Index).Tag) - 1)
'Move the cursor back one space
wsArray(Index).SendData Chr(8) & " " & Chr(8)
End If
Else
'This represents the current command. The current command is
'each character the user types in until the user presses the
'enter key.
wsArray(Index).Tag = wsArray(Index).Tag & strData(Index)
'This ECHOs the character back to the user
wsArray(Index).SendData strData(Index)
End If
Exit Sub
ErrorHandler:
'Display an error if one occurs
Dim ErrDesc As String
wsArray(Index).SendData vbCrLf & Err.Description & vbCrLf
wsArray(Index).SendData vbCrLf & "=> "
wsArray(Index).Tag = ""
End Sub
Private Sub wsListen_ConnectionRequest(ByVal requestID As Long)
'This listens for a connection and finds an open socket
Dim Index As Integer
Index = FindOpenWinsock
wsArray(Index).Accept requestID
Call ShowMenu(Index)
wsArray(Index).SendData "=> "
End Sub
Private Sub ShowMenu(Index As Integer)
'This sends the menu. We used (Index) in every instance of
'socket array because we want the data send to the appropriate
'user, in case more than one person is connected.
wsArray(Index).SendData "+-[Commands]--------------------+" & vbCrLf
wsArray(Index).SendData "| RANDOM - Display random |" & vbCrLf
wsArray(Index).SendData "| TIME - Show system time |" & vbCrLf
wsArray(Index).SendData "| HELP |" & vbCrLf
wsArray(Index).SendData "| QUIT |" & vbCrLf
wsArray(Index).SendData "+-------------------------------+" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf
End Sub
Private Function FindOpenWinsock()
'This function finds the next open socket, allowing your program
'to accept more than one connection
Static LocalPorts As Integer
'Find open socket
For X = 0 To wsArray.UBound
If wsArray(X).State = 0 Then
FindOpenWinsock = X
Exit Function
End If
Next X
'None are open so let's make one
Load wsArray(wsArray.UBound + 1)
'Let's make sure we don't get conflicting local ports
LocalPorts = LocalPorts + 1
wsArray(wsArray.UBound).LocalPort = wsArray(wsArray.UBound).LocalPort + LocalPorts
FindOpenWinsock = wsArray.UBound
End Function
Loading Comments ...
Comments
No comments have been added for this post.
You must be logged in to make a comment.